
How to Address the Talent Gap in High-Growth Industries
Table of Content
- Introduction
- Why Are High-Growth Industries Particularly Impacted?
- Defining the Talent Gap in High-Demand Sectors
- Building Skills Early: Education Partnerships That Work
- Reskilling the Workforce: Bridging Knowledge and Industry Needs
- Broadening Hiring Practices to Welcome Untapped Talent
- Collaborating With Academia to Build Expertise Pipelines
- Apprenticeships and Internships: Creating Meaningful On-the-Job Learning
- Harnessing Technology for Smarter Skill Development
- Embedding a Growth Mindset Across All Teams
- Addressing Location and Demographic-Based Challenges
- Conclusion: Turning Challenges Into Strategic Opportunities
- FAQs
Introduction
In 2023, high-growth industries face an unprecedented challenge: a widening talent gap that threatens to stifle innovation and competitiveness. This issue is magnified by rapid technological advancements and shifting socio-economic dynamics, as underscored by the World Economic Forum’s latest report, which predicts that a quarter of existing job roles will evolve significantly over the next five years. The crux of the matter lies not just in the emergence of new job requirements but also in the critical shortage of skilled personnel to fill these evolving roles.
As industries pivot towards more technology-driven models, the disconnect between current workforce capabilities and future needs becomes more pronounced. For instance, McKinsey’s 2023 Technology Trends Outlook reveals that while generative AI and advanced computing are poised to add trillions to the global economy, the lack of skilled talent remains a top constraint. This gap represents not just a barrier to technological adoption but also a strategic vulnerability in maintaining industry leadership.
The urgency to address the talent gap cannot be overstated. Recent data from Bain & Company highlights that sectors like Engineering and R&D are not only experiencing a brain drain due to attrition but are also struggling to attract young talent who prefer more dynamic roles elsewhere. The mismatch between what traditional firms offer and what the new workforce expects is at the heart of this challenge.
Moreover, demographic shifts play a significant role. As baby boomers retire, they leave behind a vacuum that the current talent pool is ill-prepared to fill due to a lag in skill acquisition and adaptability.
Why Are High-Growth Industries Particularly Impacted?
High-growth sectors such as technology, green energy, and biotech are particularly vulnerable due to their rapid pace of innovation and the specialized nature of their work. These industries require a workforce that is not only technically proficient but also agile enough to adapt to continuous changes. The talent gap in these sectors is more than just a shortage of bodies; it’s a gap in critical thinking, problem-solving, and technical skills tailored to specific futuristic needs.
The competitive edge in these industries increasingly hinges on the ability to not only foresee but also act swiftly on future skills requirements. Organizations that excel in these sectors often have robust strategies for talent management, continuous learning, and strategic hiring that keep them ahead of the curve.
From partnerships with educational institutions to fostering a culture of continuous learning and rethinking hiring practices, the focus should be on practical, actionable strategies that senior executives and HR leaders can implement to turn these challenges into strategic advantages. As we move forward, it’s essential for decision-makers to embrace a more holistic approach to talent management, viewing it not just as a function of HR but as a critical component of strategic leadership. The path forward involves a concerted effort across various dimensions of human resources, technology adoption, and corporate strategy to not only fill the current talent void but also to future-proof organizations against upcoming industry shifts.
Ready to transform your leadership landscape
Defining the Talent Gap in High-Demand Sectors
When we talk about the talent gap in industries like tech, healthcare, and green energy, it’s not just a matter of needing more hands-on deck. It’s really about the growing divide between the skills the current workforce holds and what’s needed to drive forward the next wave of business innovation and productivity. This gap isn’t just a hiccup; it’s a significant barrier to growth that companies across the globe are urgently trying to bridge.
So, what do we really mean when we talk about a ‘talent gap‘? It’s more complex than just a shortage of people. It reflects a serious shortfall in critical skills—things like advanced digital capabilities, the ability to manage new AI technologies, and the strategic acumen to navigate fast-evolving markets. We’re seeing sectors struggling to find talent in emerging fields that are crucial for future growth, such as artificial intelligence and data analytics. This isn’t just about filling positions; it’s about securing the capabilities that will define the next decade of industry leadership.
Several forces are at play here. First, there’s the rapid pace of technological change. As industries integrate technologies like generative AI, which McKinsey highlights as a transformative force across sectors, the demand for new skills skyrockets. But the supply of qualified individuals isn’t keeping up, creating a bottleneck that stifles innovation.
Then, consider demographic changes. Many sectors are seeing a wave of retirements as the baby boomer generation steps back. This isn’t just about losing bodies in the workplace; it’s about losing decades of experience and expertise. The challenge is not only to replace this workforce but to transfer their deep-seated knowledge to the next generation.
Lastly, there’s a significant lag between the skills being taught in educational institutions and those demanded by industries. This education-industry misalignment means that even when young professionals enter the workforce, they’re often not ready to hit the ground running in high-tech roles. This gap in readiness can be detrimental to sectors that depend heavily on cutting-edge skills.
The Impact on Businesses
The implications of not addressing this talent gap are far-reaching. On the operational level, companies find themselves pouring resources into training programs, trying to bring employees up to speed, rather than pushing forward with new initiatives. Strategically, the talent gap can lead businesses to miss out on critical opportunities, particularly in sectors where innovation cycles are rapid and unforgiving. But it’s not all doom and gloom. Addressing this gap provides a unique opportunity for businesses to rethink how they manage talent. By investing in training, partnering with educational institutions, and rethinking their workforce strategies, companies can turn this challenge into a competitive advantage. The key is to anticipate the skills that will be needed in the future and start cultivating them within the workforce now.
Building Skills Early: Education Partnerships That Work
The intersection of education and industry is a vibrant space where the real world meets theoretical knowledge and nowhere is this synergy more critical than in addressing the talent gaps in high-growth industries. Education partnerships, particularly those between higher education institutions and industries, are proving instrumental in equipping students with the necessary skills and competencies to thrive in today’s dynamic workforce.
How Schools and Industries Can Prepare Young Talent?
Education systems are increasingly moving away from purely theoretical frameworks and integrating real-world applications into their curricula. This shift is largely driven by the recognition that while traditional education imparts necessary foundational knowledge, it often falls short of preparing students for the specific challenges and demands of the workplace. Industry and education partnerships are a response to this gap, providing students with hands-on experiences that are not only relevant but also essential for their future careers.
These partnerships often take various forms, including co-op programs, internships, and joint research initiatives, where the focus is on practical application of learned skills. For instance, collaborations like those at GUS Canada illustrate how aligning academic learning with industry needs helps prepare students effectively for the workforce. These initiatives not only enrich the student’s learning experience but also ensure that the education they receive keeps pace with current industry standards and technologies.
Integrating practical knowledge into the educational curriculum requires a concerted effort from both educational institutions and industry leaders. This process often involves co-developing curricula that reflect the latest industry trends and requirements. For example, industries heavily invested in technology and innovation may partner with universities to offer courses that are tailored to address the skills most in demand, such as data analytics, cybersecurity, or sustainable engineering practices.
A critical aspect of these partnerships is the direct involvement of industry in educational settings. This can mean professionals from various fields participating in curriculum design, guest lecturing, or even mentoring students. Such involvement ensures that the education provided is not only current but also rich with insights from those who are actively engaged in the field.
Success Stories That Highlight Early Intervention
The positive impacts of these partnerships are evident across various sectors. For instance, health care and manufacturing sectors often engage in deep collaborations with educational institutions to address specific skills shortages. Reports show that these partnerships not only provide students with vital job training and career placement services but also enhance their employability through targeted skill development and industry exposure.
Moreover, the success of these initiatives is often measured by their ability to foster long-term relationships between students and industries, which are crucial for ongoing professional development and employment. An example of this can be seen in programs that have successfully integrated job placements as a core component of the educational experience, ensuring that students are job-ready upon graduation.
These partnerships, by bridging the gap between education and industry, play a pivotal role in preparing a workforce that is adaptable, skilled, and ready to meet the challenges of tomorrow. As we continue to witness rapid technological advancements and shifting economics, the importance of these collaborations becomes even more pronounced, signaling a robust strategy for sustaining innovation and growth within industries.
Reskilling the Workforce: Bridging Knowledge and Industry Needs
In the face of advancing technologies and shifting industries, the need for reskilling initiatives is more urgent than ever. Companies across various sectors are recognizing that to stay competitive and ensure their workforce remains relevant, they must invest in extensive training programs that not only update but fundamentally enhance the skills of their employees.
The rapid evolution of technology means that the half-life of skills is shorter than ever. Particularly in tech-heavy fields, what was relevant five years ago might now be outdated. Companies like Boston Consulting Group (BCG) emphasize that continual learning and adaptability are no longer optional but essential. In collaboration with Harvard’s Digital Reskilling Lab, BCG underscores the importance of reskilling as a strategic imperative driven by the pace of change in areas like AI and automation.
Training Programs That Align Employees with Market Demands
The most effective reskilling programs are closely aligned with current market demands. This alignment ensures that once employees undergo training, they can immediately apply their new skills effectively within their roles. For instance, Walmart and Verizon have rolled out extensive training initiatives. Walmart’s Live Better U program, for example, covers 100% of college tuition and book fees, enabling employees to gain degrees and certifications that are directly applicable to their career growth within the company. Verizon’s Skill Forward program offers free, practical training in tech-driven roles, enhancing the digital competencies of its workforce.
Successful reskilling efforts can be seen in several companies that have integrated substantial learning opportunities into their employee development programs. For example, McDonald’s Archways to Opportunity program offers comprehensive educational benefits, including tuition assistance, which supports career advancement at all levels of the organization. Another example is Google, which through its Grow with Google and Google Career Certificates initiatives, helps prepare both its employees and the wider community for tech-centric roles, focusing on areas like IT support, project management, and data analytics.
These programs highlight a significant trend: companies are not only enhancing the technical skills of their workforce but are also ensuring that these skills are directly applicable to current and future job markets. By investing in reskilling, these organizations are effectively future-proofing their employees, enabling them to navigate new technologies and industry standards that are rapidly reshaping their fields.
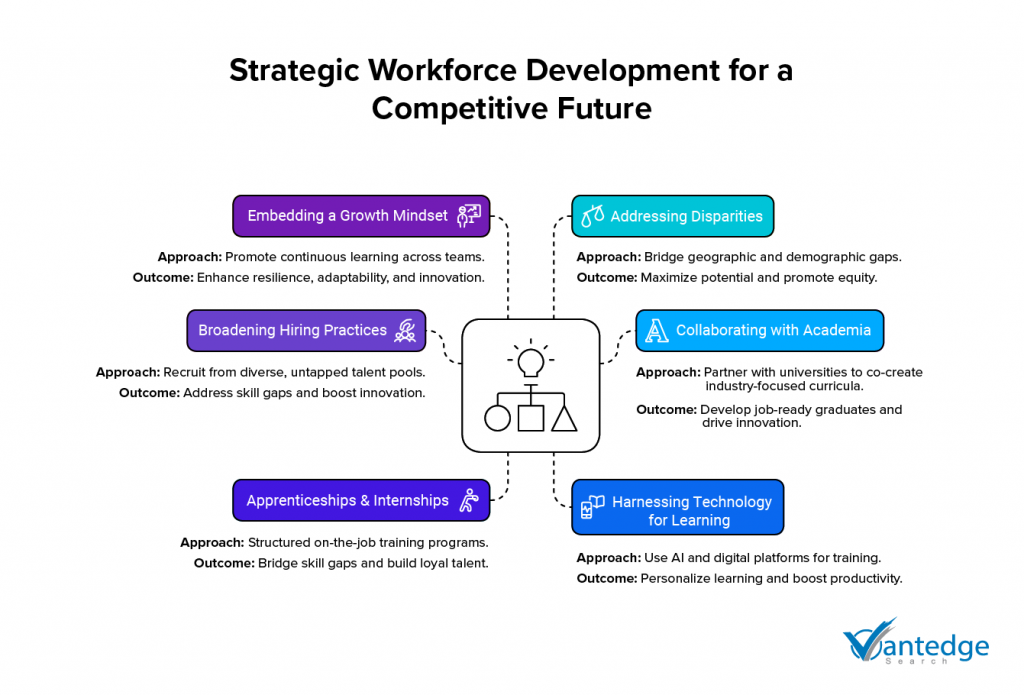
Broadening Hiring Practices to Welcome Untapped Talent
In an increasingly competitive global market, broadening hiring practices to include overlooked talent pools has become a strategic imperative for businesses aiming to innovate and grow sustainably. By diversifying recruitment efforts, companies not only address skill gaps but also enhance their workplace culture and drive creativity.
Modern businesses are increasingly recognizing the value of tapping into diverse talent pools that were previously overlooked. This includes reaching out to groups such as returnees to the workforce, individuals from different cultural or socio-economic backgrounds, and people living with disabilities. For instance, the UK government’s “returnership” initiative specifically encourages those over the age of 50 to re-enter the workforce, providing a pathway back to employment and addressing the skill shortages in various sectors.
Furthermore, companies are casting a wider net by embracing remote work capabilities, allowing them to engage with talent globally without geographical constraints. This approach not only fills vacancies for highly skilled individuals but also brings varied perspectives that can lead to greater innovation and adaptation to global market needs.
The Benefits of Inclusive Hiring Practices
The advantages of implementing inclusive hiring practices extend far beyond filling vacancies. Organizations that prioritize diversity and inclusivity in their hiring processes often see a range of benefits, including enhanced creativity, better problem-solving capabilities, and improved product development outcomes. A diverse workforce brings a variety of perspectives that can lead to innovative solutions and services that cater to a broader customer base.
Moreover, companies that actively recruit from a wide range of backgrounds are likely to see improved employee engagement and satisfaction. Employees tend to feel more valued and included when they see a genuine commitment to diversity in their workplace. This not only improves morale but also boosts retention rates and reduces the costs associated with high turnover.
Incorporating diverse recruitment strategies, such as skills-based hiring and the expansion of recruitment channels, helps businesses align more closely with contemporary labor market dynamics. By focusing on skills and competencies rather than just credentials, companies can uncover talent with a wide range of experiences that might otherwise have been overlooked due to traditional hiring biases.
Collaborating With Academia to Build Expertise Pipelines
The intertwining of academic institutions with industry is becoming increasingly crucial for long-term industry growth and innovation. These partnerships are not just enhancing the educational prospects but are also ensuring that the workforce is ready to meet future challenges with relevant skills and knowledge.
Industries are increasingly seeing the value in forming partnerships with universities as a strategic approach to foster innovation and sustain growth. These collaborations often begin with targeted projects or workshops and ideally evolve into long-term commitments that are beneficial for both parties. By aligning their resources, universities and industries can drive advancements in research and development, which in turn fuels economic growth and competitiveness on a global scale.
One of the most tangible benefits of university-industry collaborations is the co-designing of courses that cater directly to the needs of the industry. By integrating real-world projects and challenges into the curriculum, students gain practical experience and insights into the demands of their future careers. For instance, industries like engineering and technology are collaborating with academic institutions to ensure that the curriculum reflects the rapidly evolving needs of the sector, providing students with the skills that are in critical demand.
Demonstrated Outcomes from Effective Academic Partnerships
The outcomes of these collaborations can be seen in various forms, from enhanced student employability to groundbreaking research that solves real-world problems. For example, industry partners often participate in curriculum development, ensuring that what is taught is directly relevant to current industry goals. This not only prepares students to be more effective in their roles upon graduation but also enhances the university’s reputation as a leader in producing ready-to-work graduates.
Moreover, these partnerships often lead to the creation of innovation hubs where theoretical knowledge meets practical application, driving forward both technological advancements and new business solutions. The ongoing exchange of knowledge and resources between academia and industry ensures that educational programs keep pace with industry changes, making the graduates highly desirable in the job market.
Apprenticeships and Internships: Creating Meaningful On-the-Job Learning
Apprenticeships and internships are proving to be invaluable for both employers and trainees in today’s fast-paced work environment. They offer real-world exposure and experience which are crucial not just for personal development, but also for meeting the evolving needs of industries.
Effective apprenticeship programs are structured to provide value both to the participants and the companies that host them. For example, Brookings highlights the importance of structured earn-and-learn opportunities that include clear pathways for progression, which benefit not only the learners but also the industries by addressing specific skill shortages. Programs are most successful when they align closely with industry needs, ensuring that the training is relevant and that participants are ready to contribute effectively upon completion.
Harnessing Technology for Smarter Skill Development
The shift towards digital tools in employee learning is unmistakable. Organizations are increasingly adopting digital platforms that offer interactive, on-demand, and personalized learning experiences. These platforms are designed to engage employees in a variety of learning formats—from microlearning sessions that cater to immediate skill needs to comprehensive training programs designed for deep skill development. This approach not only accommodates the varying paces at which individuals learn but also aligns with their specific career trajectories and learning preferences.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing a pivotal role in customizing training to meet individual needs. AI-driven platforms can analyze a learner’s performance in real-time, adapting the curriculum to address weaknesses or to skip over known material. Microsoft, for example, has emphasized the necessity for AI proficiency among employees, suggesting that integrating AI can significantly enhance productivity and creative capabilities by relieving employees from repetitive tasks and allowing more time for innovation.
The benefits of integrating technology into skill development are significant and quantifiable. For instance, organizations that employ digital learning tools and AI are seeing improvements in employee engagement and retention rates. Deloitte highlights that skills-based digital workplaces, which leverage digital tools for training and development, are more likely to retain high performers and innovate effectively.
Embedding a Growth Mindset Across All Teams
Fostering a growth mindset within an organization isn’t just about personal development; it’s about creating a culture that enhances overall team performance, innovation, and adaptability. This approach encourages continuous learning and resilience, crucial for organizations aiming to thrive in a rapidly changing world.
Leaders play a pivotal role in embedding a growth mindset by modeling behaviors that promote continual learning and adaptability. A leader who embraces challenges, encourages experimentation, and views failures as learning opportunities can profoundly influence their team’s approach to work. This culture of learning and improvement fosters an environment where employees are motivated to develop their skills continuously and adapt to new challenges effectively. Organizations like Microsoft have transformed their cultures by encouraging leaders to adopt a growth mindset, which has led to enhanced creativity and innovation across the board.
Motivating employees for lifelong learning involves integrating growth mindset principles into everyday practices. This can be achieved by prioritizing learning and development through structured programs and embedding learning opportunities into the flow of work. For example, providing access to training sessions, workshops, and digital learning platforms can help employees align their personal growth with organizational goals. Companies like Avanade and The Wonderful Company have successfully implemented strategies that encourage continuous learning, showing significant improvements in employee engagement and workplace satisfaction.
Several organizations have been recognized for their effective learning cultures. For instance, at Microsoft, the shift from a “know-it-all” to a “learn-it-all” culture has not only enhanced individual employee growth but also driven corporate success. This change was facilitated by leadership that emphasized openness to new ideas and constructive feedback, encouraging a company-wide embrace of learning and development.
Addressing Location and Demographic-Based Challenges
Tackling geographic and demographic disparities in the workforce is crucial for businesses that aim to harness the full potential of diverse talent pools and ensure equitable opportunities across different regions.
Geographic disparities often manifest in unequal economic opportunities, making it essential for companies to adopt strategies that address these imbalances. For instance, the U.S. Department of Commerce highlights the widening geographic inequality over the past decades, suggesting targeted government programs to mitigate these disparities. In the healthcare sector, initiatives like HHS’s efforts to improve access in rural areas through grants and technical assistance demonstrate how targeted investments can bolster regional services and infrastructure.
Addressing the challenges faced by underrepresented demographics requires focused outreach and program development. Efforts to bridge the gender gap in employment, as noted by the Center for American Progress, show the importance of addressing occupational segregation and supporting women through policies that facilitate easier reentry into the workforce and continued employment. Similarly, Deloitte discusses the significance of diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives that not only aim for diverse recruitment but also ensure equitable outcomes, emphasizing actions that genuinely support the professional advancement of underrepresented groups.
Conclusion: Turning Challenges Into Strategic Opportunities
As we navigate the complexities of today’s talent scenarios, decision-makers must pivot challenges into strategic opportunities for growth and innovation. By synthesizing the insights gathered, we can outline actionable advice that leaders can utilize to enhance their organizational strategies effectively.
Looking ahead, the path forward involves a concerted effort to not only address immediate talent shortages but also to anticipate future needs. This requires a proactive approach to workforce planning, where skills forecasting and strategic workforce developments are integrated into the core business strategy. By focusing on sustainable and adaptable workforce strategies, companies can ensure they are well-positioned to meet the challenges of the future, turning potential vulnerabilities into vectors for growth and innovation.
FAQs
The talent gap refers to the mismatch between the skills currently available in the workforce and those needed to meet the evolving demands of industries like technology, healthcare, and green energy. This shortage of skilled professionals creates significant challenges for innovation and competitiveness.
High-growth industries often experience rapid technological advancements and require specialized skills. This accelerates the demand for a workforce capable of adapting to change, leaving a wider talent gap in critical areas like AI, data analytics, and renewable energy.
Organizations can tackle the talent gap by investing in reskilling programs, collaborating with educational institutions, and adopting inclusive hiring practices. These strategies help bridge the skill gap while preparing the workforce for future challenges.
Educational partnerships align academic programs with industry needs by introducing practical learning opportunities like internships, co-op programs, and tailored curricula. These initiatives equip students with the skills required to address the talent gap in high-demand sectors.
The retirement of experienced baby boomers has left a skills vacuum that newer workforce entrants are often unprepared to fill. Combined with the lag in education systems aligning with industry needs, these demographic changes exacerbate the talent gap.


Leave a Reply