
Introverted Leadership: Harnessing Silent Strength in an Extroverted World for Leadership Diversity
Table of Content
- Introduction
- Introverted Leaders: Values, Challenges, and the Need for Synergistic Leadership
- The Strategic Edge of Introverted Leadership: Corporate Titans and Visionaries
- Empowering Strategies for Introverted Leaders
- Maximizing Introverted Leadership: Strategies for Organizational Success
- Conclusion: Embracing a New Era of Leadership Diversity
Introduction
“I think introverts can do quite well. If you’re clever, you can learn to get the benefits of being an introvert.” – Bill Gates
Is the loudest voice always the most effective? Despite the traditional celebration of charismatic, extroverted leaders in business, emerging trends and evolving workplace demands are challenging this archetype. A surprising statistic from Psychology Today reveals that while 96% of business leaders identify as extroverted, their extroverted traits—like charisma—do not necessarily equate to better performance. In fact, studies show that introverts are often just as effective, if not more so, in leadership roles.
The gap between perception and reality is particularly pronounced today, characterized by hybrid work models, rapid technological advances, and ongoing global crises. These scenarios demand leaders who are not only charismatic but also thoughtful, reflective, and strategic in their approach to address the challenges in leadership.
This blog delves into the often-overlooked strengths of introverted leaders, offering insights and strategies on how they can thrive and how organizations can harness these qualities for strategic advantage through a balanced leadership approach.
Struggling to Find the Right Leader?
Introverted Leaders: Values, Challenges, and the Need for Synergistic Leadership
Strengths of Introverted Leaders
Introverted leaders bring a unique set of strengths to the corporate table, including deep strategic thinking, empathetic engagement, and the ability to build strong, cohesive teams through meaningful one-on-one interactions. Their natural inclination towards reflection and deliberation in decision-making ensures that actions are carefully considered, often leading to more sustainable outcomes and inclusive leadership development. Introverts excel at fostering a culture of trust and innovation by creating environments where diverse perspectives are valued.
Challenges Faced by Introverted Leaders
Despite their unique strengths, introverted leaders often encounter significant obstacles. The pervasive stereotype that equates leadership with extroversion can lead to the undervaluation of their contemplative and introspective qualities. These leaders may struggle with visibility, as their lower propensity to self-promote can result in their contributions being overlooked in environments that favor outspoken behavior.
Additionally, their careful deliberation can be misinterpreted as hesitancy in high-energy settings, and the fast-paced nature of modern workplaces can be particularly taxing, increasing the risk of burnout. Recognizing the challenges faced in leadership by introverts is crucial for organizations aiming to support these leaders effectively.
Synergistic Leadership Approach
The key difference between introverted and extroverted leaders lies in their inherent personality traits that define their unique leadership approach. While introverts naturally excel in reflective and empathetic approaches, extroverts thrive in dynamic, high-energy environments with broad engagement.
These differences, however, are not rigid; leaders from both spectrums can develop each other’s qualities through leadership development and soft skills programs. The business environment is evolving, characterized by hybrid work models and rapid technological change; this underscores the need for a balanced approach that leverages the strengths of both personality types. As the conventional dominance of extroverted leadership gives way, the importance of nurturing introverted leadership capabilities becomes increasingly apparent.
The Strategic Edge of Introverted Leadership Approach: Corporate Titans and Visionaries
Introverted leaders across industries demonstrate how deep thought, reflective decision-making, and a preference for meaningful one-on-one communications can significantly influence and transform sectors (source: Career Addict). Often underestimated in fast-paced, extroverted environments like politics and technology, the unique strengths of introverted leaders are crucial for navigating complex challenges and fostering innovation.
Barack Obama – Strategic Calm in Leadership:
Celebrated for his eloquence, former President Obama exemplifies introverted leadership in the extroverted arena of politics. Beyond his public speeches, he exhibited a calm, composed nature, preferring thoughtful deliberation over quick decisions—a style that effectively managed complex global issues and balanced public engagement with reflective strategy.
Steve Wozniak – Solitude as a Catalyst for Innovation:
As the co-founder of Apple, Wozniak credits his innovative prowess to his introverted disposition. His preference for working alone fueled the creation of Apple’s first line of products, challenging the conventional collaborative innovation model and setting the foundation for one of the most successful technology companies in the world.
Marissa Mayer – Quiet Leadership in Silicon Valley:
The former CEO of Yahoo, Mayer is known for her quiet, introspective leadership approach. Her style of listening more than speaking helped her navigate numerous corporate challenges at Yahoo, demonstrating how introverted qualities can lead to successful outcomes in competitive environments.
Larry Page – Leadership Behind the Scenes:
Co-founder of Google and later CEO of Alphabet, Page uses his introverted traits to lead one of the most influential tech companies globally. Known for his reserved and reflective nature, he focuses on innovation and creativity, enabling his teams to excel by emphasizing the bigger picture.
These examples highlight the strength of introverted leadership styles, especially in settings that traditionally favor extroversion. Their success underscores the need for corporate cultures to embrace and support leadership diversity, including those styles that thrive in thoughtful solitude and reflective deliberation.
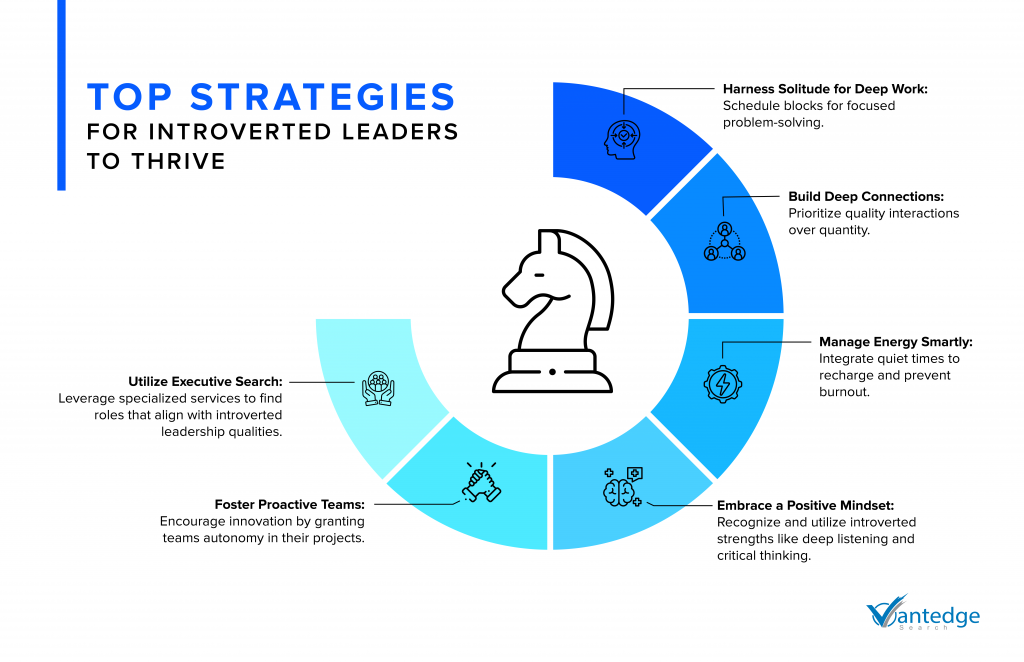
Empowering Strategies for Introverted Leaders
Introverted CEOs and leaders thrive in deep thought, careful planning, and forging strong one-on-one relationships. According to Get Lighthouse, a management consulting platform, the unique strengths of introverted leaders can be strategically leveraged for leadership success.
Harnessing the Power of Solitude
Introverted leaders are adept at deep thought and solitary problem-solving. Bill Gates exemplifies this by retreating to focus intensely on complex issues before presenting solutions—a hallmark of effective introverted leadership.
In line with this, introverted leaders could create a schedule that prioritizes deep work, minimizes interruptions, and capitalizes on peak concentration hours to tackle significant challenges.
Deepening Connections: Networking That Matters
Instead of broad social networking, introverts thrive on deep, meaningful interactions. Douglas Conant, the former CEO of Campbell’s Soup, transformed his company’s culture by engaging employees through personalized interactions like thank-you notes.
Similarly, introverted leaders should seek genuine connections in smaller, intimate settings that foster deeper conversations and stronger bonds.
Mastering Energy Management
Frequent social interactions can be draining for introverts. Leaders like Conant managed their energy by scheduling quiet times and preferring written communications to recharge between engagements.
Introverted leaders should identify their most draining activities and structure their schedules to include regular breaks and quiet periods to sustain their productivity and well-being.
Cultivating Confidence in Quiet Strength
Introverts often underestimate their impact due to societal biases favoring extroversion. However, embracing a positive outlook on their capabilities can significantly enhance their leadership effectiveness. By focusing on their strengths, such as deep listening and critical thinking, introverted leaders can leverage these traits as powerful assets.
Fostering a Culture of Proactive Innovation
Proactive team environments are ideal for introverted leaders. William McKnight of 3M, for instance, promoted a culture of innovation by allowing employees to dedicate time to personal projects.
Introverted leaders would do well to promote autonomy and encourage open communication and idea sharing, supporting their teams in taking initiative.
Strategic Career Advancement with Executive Search
Leveraging services like Vantedge Search is an effective leadership approach for introverted leaders. These companies play a crucial role in positioning introverted leaders in roles that match their strengths, such as strategic thinking and independent work.
They undertake tailored leadership assessments that are helpful in placing introverted leaders in environments where they can lead effectively, whether in roles that oversee smaller teams or require substantial strategic planning.
Maximizing Introverted Leadership Approach: Strategies for Organizational Success
Understanding how introverted leaders leverage their unique strengths represents only one facet of their impact. The other, equally critical aspect involves how organizations proactively harness this potential for leadership diversity and inclusive leadership development. Here are some strategies that allow organizations to fully benefit from the quiet power of introverted leadership.
A. Cultivating Inclusive Leadership Development
Strategic Depth Through Solitude
Establish strategy retreats dedicated to deep strategic planning in quiet, distraction-free environments where introverted leaders can engage extensively in long-term planning.
Additionally, create thought leadership forums that prioritize written communication and thoughtful dialogue, allowing introverted leaders to present well-researched insights and strategies.
This setup ensures that introverted strengths are utilized effectively in generating and sharing knowledge.
Enhancing Integrative and Reflective Thinking
Implement structured reflective breaks throughout the workday to allow introverted leaders to process information and generate innovative ideas, incorporating practices like mindfulness and silent contemplation.
Organize problem-solving workshops that leverage introverted leaders’ strengths in deep analysis, using techniques like the Delphi method to ensure all voices are heard without the pressure of immediate interaction.
Building Cognitive Diversity
Form task forces with a mix of cognitive styles to balance deep thinking with dynamic execution and assign roles that align with the cognitive strengths of introverted leaders, such as risk assessment and strategic foresight.
This approach helps maximize the analytical and reflective skills of introverted leaders in various strategic contexts.
Role Modeling Non-Discriminatory Leadership
Promote a culture that values both introverted and extroverted traits equally by ensuring leadership models and behaviors within the organization do not favor one over the other.
Develop inclusive programs that provide equal opportunities for introverted leaders to advance, highlighting and celebrating their successes to set a positive example and encourage recognition of diverse leadership styles.
B. Embracing Diverse Executive Recruitment
Utilizing Predictive Behavioral Analytics and Innovative Partnerships
Use advanced behavioral profiling tools to identify introverted leaders who may not be immediately visible through traditional recruitment methods, developing recruitment metrics that include contextual and situational assessments.
Collaborate with executive search firms to run recruitment drives specifically targeting introverted leadership traits. This would pivot on emphasizing the importance of introspective and empathetic qualities in job descriptions. It could also help in creating leadership development pipelines that nurture introverted talent from within the organization.
C. Creating Supportive Work Environments
Designing Adaptive Workspaces and Building Psychological Resilience
Design adaptive work environments that cater to the sensory needs of introverted leaders, including options for quiet zones, personalized lighting, and soundproof spaces to enhance focus and productivity.
Offer flexibility in work locations, allowing leaders to choose settings that best suit their work style.
Implement resilience programs tailored to the needs of introverted leaders, incorporating techniques like cognitive-behavioral strategies and mindfulness meditation, and provide emotional intelligence training to help leaders navigate interpersonal dynamics while maintaining their authenticity.
Enhancing Reflective Decision-Making
Introduce silent brainstorming sessions where ideas are submitted in writing before group discussions, ensuring that introverted leaders have time to articulate their thoughts without the pressure of immediate verbal exchange.
Establish decision-making labs where introverted leaders can experiment with different models and techniques in a controlled, low-pressure environment, refining their decision-making skills through reflective practice.
D. Leveraging Strengths in Succession Planning
Fostering Long-Term Vision and Strategic Succession
Include introverted leaders in succession planning committees where their long-term vision and strategic depth can contribute significantly to identifying and grooming future leaders.
Develop mentorship programs where seasoned introverted leaders mentor emerging talent, ensuring that reflective and thoughtful leadership qualities are passed on to the next generation.
Establishing Equal Opportunity Frameworks
Create transparent evaluation criteria for leadership roles that equally value the strengths of introverted leaders, helping to ensure that introverted candidates are considered fairly for advancement and key positions.
Implement balanced leadership development programs that cater equally to the growth and advancement of both introverted and extroverted leaders.
By adopting these innovative and deeply insightful strategies, organizations can fully leverage the unique strengths of introverted leaders, creating a more balanced, inclusive, and dynamic leadership landscape.
Conclusion: Embracing a New Era of Leadership Diversity
Embracing a diversity of leadership styles has become crucial for organizational success amid the increasing complexity of the global business landscape. This has notably elevated the significance of the introverted leadership approach, which was previously overshadowed by the extroverted style.
As trends evolve, the future of effective leadership is increasingly seen to depend on a balanced approach— one that combines the dynamic, outward-facing qualities of extroverted leaders with the reflective, strategic depth of introverted leaders. This synergy sets a new standard for success and innovation, redefining what it means to lead effectively in the modern business environment.
Looking to unlock the potential of introverted leadership in your organization? Connect with Vantedge Search to discover leaders who can transform your business landscape. Contact us now!


Leave a Reply